Severe Knee Joint Pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, arthritis, and other medical conditions. If you’re experiencing Severe Knee Joint Pain you have access to a wide range of healthcare facilities and professionals who can help diagnose and treat your condition
1.Causes of Severe Knee Joint Pain:
Injuries:
Ligament Injuries: Tearing of ligaments like the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) often occurs during sports activities and can cause Severe Knee Joint Pain and instability.
Meniscus Tears: The meniscus is cartilage in the knee that can tear from twisting motions, commonly during sports and cause Severe Knee Joint Pain.
Fractures: Severe pain in Knee Joint can be due to Bones in the knee, including the patella (kneecap), fracture in accidents or falls.
Dislocations: The kneecap can be dislocated, often due to trauma.
Medical Conditions that cause Severe Knee Joint Pain:
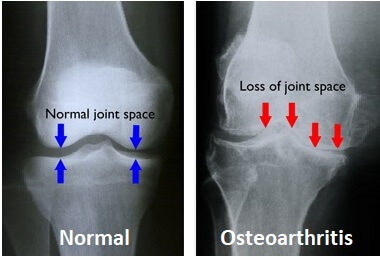
- Arthritis: There are different types, such as osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease), rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune condition), and gout (caused by uric acid crystals).
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee).
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons, often from overuse, especially in sports or repetitive activities.
- Overuse and Repetitive Strain: Activities that put repetitive stress on the knee joint, such as running, jumping, or cycling, can cause pain and conditions like patellar tendinitis or iliotibial band syndrome.
- Infections: Though less common, infections can cause knee pain and swelling.
- Osgood-Schlatter Disease: Often occurs in adolescents, involving inflammation of the area below the kneecap where the tendon from the kneecap attaches to the shinbone.
2. Symptoms Associated with Severe Knee Joint Pain:
- Swelling and Stiffness: The knee may appear swollen, and there might be a limited range of motion.
- Redness and Warmth: These symptoms suggest inflammation or infection.
- Weakness or Instability: Difficulty standing, walking, or feeling as though the knee might “give way
- Popping or Crunching Noises: These sounds might accompany movements if there is a structural issue in the knee
- Inability to Fully Straighten the Knee: This can be due to swelling, injury, or structural damage.
3. Diagnosis and Treatment of Severe Knee Joint Pain:
Diagnosis:
A healthcare provider may use physical examination, imaging tests like X-rays, US Scan, MRI, or CT scans, and sometimes blood tests to diagnose the cause of knee pain.
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatments for Severe Knee Joint Pain:
Rest and Activity Modification:
- Rest: Giving the knee time to heal, especially if the pain is due to an injury or overuse.
- Activity Modification: Reducing or avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain, such as high-impact sports or repetitive bending.
Ice or Heat Therapy:
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the knee can help reduce swelling and numb the area, providing pain relief, especially soon after an injury
- Heat: Applying heat can relax and loosen tissues, and stimulate blood flow to the area. It’s usually more helpful for chronic conditions.
Medications:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Topical Pain Relievers: Creams or gels applied directly to the skin over the knee may help alleviate pain
- Prescription Medications: For more severe pain, doctors may prescribe stronger pain medications or corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can design a program to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and restore function. This can help reduce Severe pain in Knee Joint and prevent future injuries.
Supportive Devices:
- Braces or Supports: Knee braces can help stabilize the knee and protect it from further injury.
- Orthotic Shoe Inserts: Custom or over-the-counter inserts can help correct misalignment and reduce stress on the knee joint
Invasive Treatments:
Injections:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Can provide relief from inflammation and pain, particularly for conditions like arthritis.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: These can lubricate the knee joint, often used for osteoarthritis.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Other Biologic Treatments: These newer treatments use components from your own blood to promote healing.
Surgical Options:
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgery where a small camera and instruments are inserted into the knee to diagnose and treat problems such as meniscus tears, ligament injuries, or cartilage damage.
- Partial Knee Replacement: Replacing only the damaged part of the knee, preserving as much of the natural knee as possible.
- Total Knee Replacement: The entire knee joint is replaced with an artificial joint, typically for severe arthritis or damage that doesn’t respond to other treatments.
3. Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
Weight Management:
- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on the knee joints and can alleviate pain, particularly for conditions like osteoarthritis.
Exercise and Strengthening:
- Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking can strengthen the muscles around the knee without putting excessive strain on the joint.
- Stretching: Regular stretching can help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness.
Diet and Supplements:
- A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (like fish, nuts, and leafy greens) and possibly supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin may support joint health.
4. Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: Some people find relief through acupuncture, which involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body.
- Massage Therapy: Can help relieve muscle tension and improve circulation.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the specific cause and Severe Knee Joint Pain. They can provide a diagnosis and recommend the best course of action tailored to your needs.